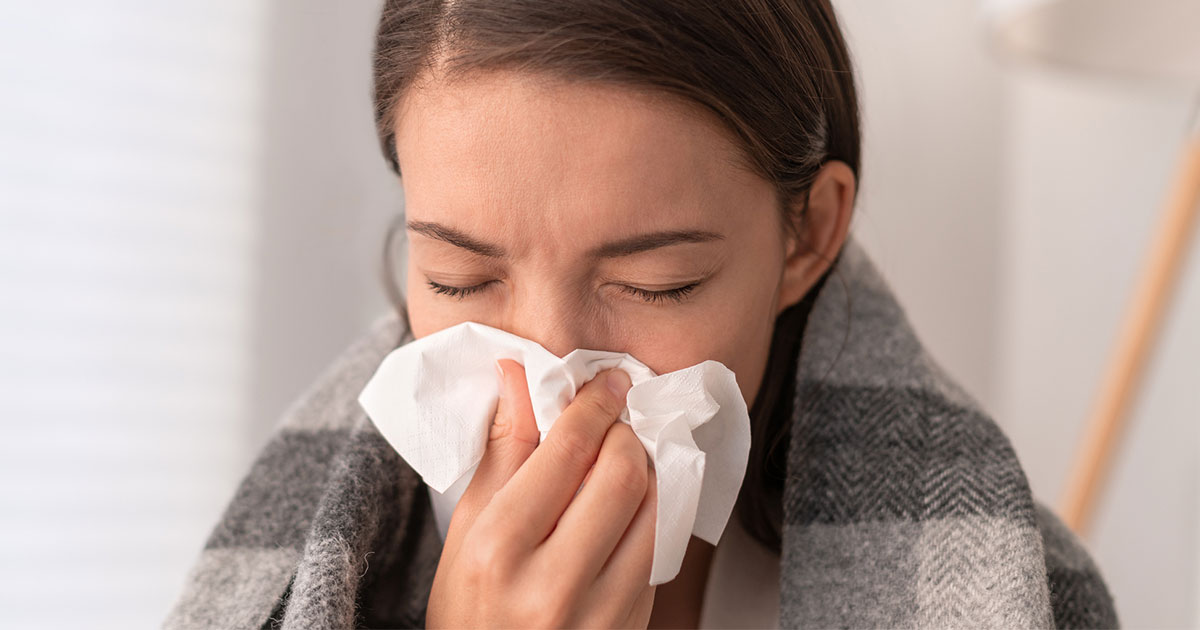
What is influenza? Influenza is commonly known as the “flu.” The flu is caused by influenza viruses that infect the nose, throat, and lungs. Flu symptoms can range from mild too severe, and in some cases can cause death.
Who is at greatest risk for the flu? Individuals 65 years and older, anyone with chronic diseases, pregnant women, and children.
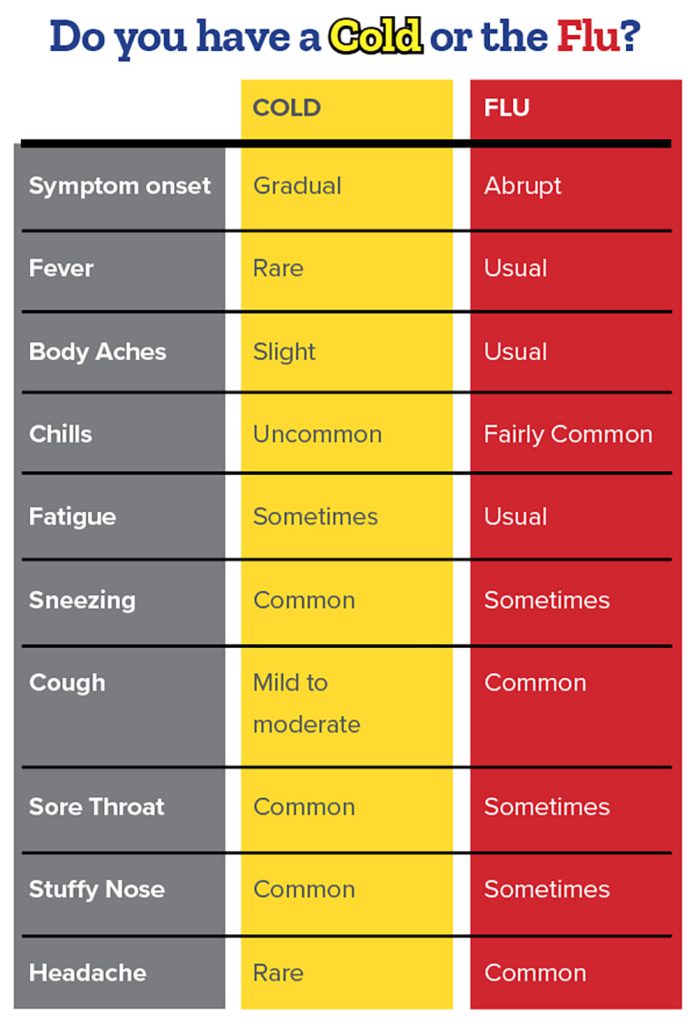
How long after I am exposed to the flu will symptoms begin? Symptoms begin from 1 to 4 days after exposure to the flu.
How is the flu spread? Flu is mainly spread in droplets when infected people cough, sneeze, or talk; however, flu can also be spread by touching frequently touched surfaces and then touching one’s mouth, nose, or eyes.
How long will I be contagious? The flu may be passed to others one day BEFORE symptoms appear and up to 5 to 7 days AFTER symptoms start.
How is the flu diagnosed? The most common method used to diagnose the flu is a “rapid flu test,” which involves swabbing the inside of your nose/back of throat to obtain a specimen that is tested onsite at the clinic. The results are available approximately 15 minutes after collection of the specimen.
Are there ways to treat the flu?
- Antiviral drug for 5 days; best started within 48 hours of start of symptoms
- Increase fluids
- Warm, salt water gargles to relieve sore throat
- Rest
- Over-the-counter medications for cough, fever, body aches
- Warm mist / steam to relieve congestion
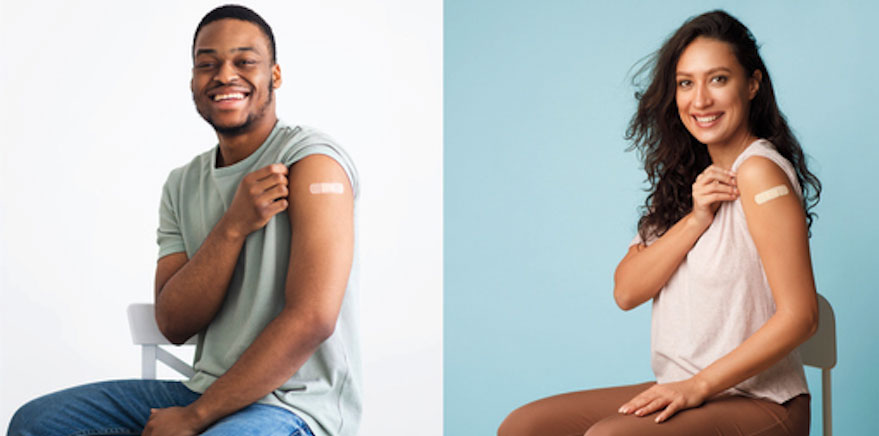

Three actions to prevent or lessen the flu.
1. Take time to get a flu vaccine.
- CDC recommends a yearly flu vaccine as the first and most important step in protecting against flu viruses.
- Everyone 6 months and older should get an annual flu vaccine, ideally by the end of October.
- This season, all flu vaccines will be designed to protect against the four flu viruses that research indicates will be most common.
- Vaccination of people at higher risk of developing serious flu complications is especially important to decrease their risk of severe flu illness.
- Flu vaccines help to reduce the burden of flu illnesses, hospitalizations and deaths on the health care system each year.
- Vaccination also is important for health care workers, and other people who live with or care for people at higher risk to keep from spreading flu to them. This is especially true for people who work in long-term care facilities, which are home to many of the people most vulnerable to flu.
2. Take everyday preventive actions to stop the spread of germs.
- Take everyday preventive actions that are recommended to reduce the spread of flu.
- Avoid close contact with people who are sick.
- If you are sick, limit contact with others as much as possible to keep from infecting them.
- Cover coughs and sneezes.
- Wash your hands often with soap and water. If soap not available, use an alcohol-based hand sanitizer.
- Avoid touching your eyes, nose and mouth.
- Clean and disinfect surfaces and objects that may be contaminated with viruses that cause flu.
3. Take flu antiviral drugs if your doctor prescribes them.
- If you are sick with flu, antiviral drugs can be used to treat your illness.
- Antiviral drugs are different from antibiotics. They are prescription medicines (pills, liquid or an inhaled powder) and are not available over-the-counter.
- Flu antiviral drugs can make flu illness milder and shorten the time you are sick. They may also prevent serious flu complications.
- Studies show that flu antiviral drugs work best for treatment when they are started within 2 days of getting sick, but starting them later can still be helpful, especially if the sick person has a higher risk factor or is very sick from flu.
- If you are at higher risk from flu and get flu symptoms, call your health care provider early so you can be treated with flu antivirals if needed. Follow your doctor’s instructions for taking this drug.
©2022HealthSpot References: Information contained in this issue is from the CDC (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website (cdc.gov).

